Table of Content
Your direct and indirect home office expenses are treated differently. You can also work outside your home and claim the deduction. One of the main requirements you must meet is using a certain part of your home on a consistent basis for your business. For example, you might choose to work from a guest room, a detached garage, or any identifiable space. You must satisfy usage requirements to claim the deduction. Logan is a practicing CPA and founder of Choice Tax Relief and Money Done Right.

You can spread out the cost of the purchase over a number of years. Mrinalini is the senior investing editor at The Balance and is an expert in investing, financial journalism, digital media, and more. She's been a journalist for more than 10 years at organizations such as the Financial Times and Investopedia, and she has a master's in business and economic reporting from New York University. I consent to Timpe CPAs collecting my details through this form.
Selling Your Home, Gains, and Depreciation Recapture
In this case, you could write off $1,500 using the simplified method (300 square feet x $5). But if your business is located in a 600-square-foot finished basement, the deduction is still $1,500 due to this method’s deduction cap. The IRS allows businesses to deduct expenses that are ordinary and necessary to their operation. It follows a similar methodology for home office deductions. But remember, you can only deduct business expenses and not personal expenses, so while you share the premises, you will have to account for business expenses separately. To qualify under prior law, a home office had to be used for the “convenience” of your employer.
There's no specific definition of what constitutes regular use. Clearly, if you use an otherwise empty room only occasionally and its use is incidental to your business, you'd fail this test. If you work in the home office a few hours or so each day, however, you might pass. This test is applied to the facts and circumstances of each case the IRS challenges. How can internal auditors provide oversight of their organizations’ cryptocurrency and blockchain usage? In addition, the wind caused a tree to fall through the picture window in your family room, which is not part of your home office.
Determining if an expense is deductible.
The tax rules on how to write-off office expense deductions can be confusing. To claim a casualty loss you must file a timely claim for any insurance you have on the property, and you can only deduct the portion of the loss that is not reimbursed by insurance. Anne determines that $250 of the bill is for lighting alone. Because she uses 10 percent of the house for business, $25 may be deductible as a business expense.
The cost of any improvements before and after you began using your home for business. The space used is separately identifiable and suitable for storage. It means that your home office must be where you spend the most time and where you complete most of the important business tasks. We may receive a commission if you sign up or purchase through links on this page. You physically meet with patients, clients or customers on your premises.
Rental Property Depreciation: How to Depreciate Rental Property
Wondering whether you should deduct actual expenses or use the simplified method? We can help you determine what’s right for your specific situation. Section 179 usually produces the largest deduction because you're claiming the entire cost all at once. This reduces both your income tax and your self-employment tax.
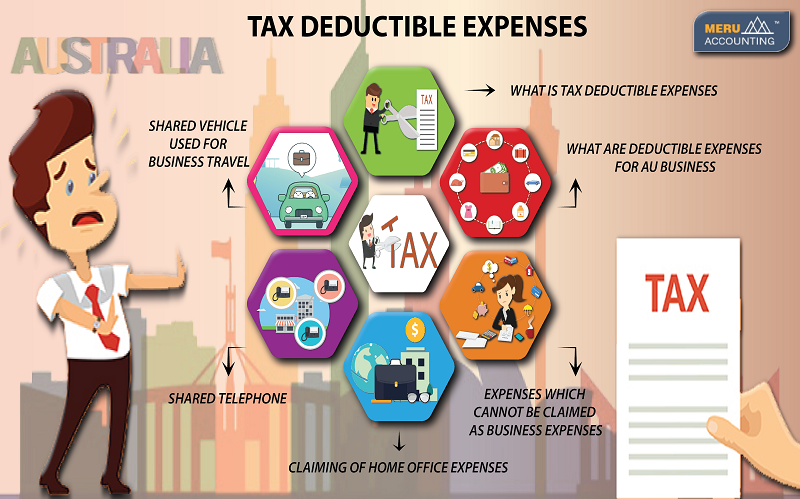
For instance, you might also work occasionally at a coffee shop, a co-working space, or meet clients in their homes. However, starting with the 2018 tax year, you’re no longer allowed to claim a home office deduction unless you’re self-employed. So, if you’ve grown accustomed to writing off a variety of expenses related to working from home as an employee, it’s no longer allowed. You don’t have to calculate depreciation to claim the home office deduction if you use the simplified method.
Your maximum allowed deduction is $2000, but you have $4000 in home office expenses that you still want to deduct. You can therefore only deduct up to the $2000 deduction limit and will have to carry over $2000 ($4000-$2000) to the next tax year. The following is an example of how to use your income and expenses to determine your home office deduction allowed in a tax year. If you use one to run your business, you may be able to take certain deductions on your taxes. However, you need to meet certain eligibility criteria and may be subject to a limit on how much you can deduct.

For the 2019–20 income year, if you worked from home before 1 March 2020, you may need to use more than one of the three methods to work out your total deduction for the year. Use our home office expenses calculators to work out your claim for work-related expenses you incur as a result of work you do from home as an employee. An easier calculation is acceptable if the rooms in your home are all about the same size.
The maximum tax refund you can get is largely dependent on your individual income and filing status. Generally, the more money you make and the more deductions you take, the higher your refund amount will be. Additionally, tax credits and deductions can significantly increase your refund amount.
The 20% business tax deduction is a provision of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act that allows certain businesses to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income from their taxable income. This deduction applies to businesses that are organized as pass-through entities, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, and S-corporations. Itemized deductions are a list of expenses that can be used to reduce your taxable income if the total of the expenses is more than your standard deduction. Itemized deductions include medical bills, charitable donations, mortgage interest payments, and more. You would apply your percentage rate to each of these expenses, then tally them up to arrive at your deduction.
For example, if it’s 10% of your home, you can attribute 10% of qualifying expenses to business use. If it qualifies as a trade or business, then you can claim the home office deduction. If you sell your home, you’ll need to recapture any depreciation you deducted or could have deducted from your tax return if you used the actual expense method. Using your home for business allows you to claim depreciation expense. It can increase your home office deduction and decrease your taxable income. For example, if you use 200 square feet for business, you’ll deduct $1,000 ($5 x 200) for business expenses.

After spending nearly a decade in the corporate world helping big businesses save money, he launched his blog with the goal of helping everyday Americans earn, save, and invest more money. In addition to documents showing the original purchase price of your home, you’ll need to keep all receipts for permanent improvements. New roof, new windows, replaced HVAC, or upgraded water heater all qualify as permanent improvements. But if you claimed a home office deduction for business use of your home, things are a little trickier. However, the simplified method is better for those who dread recordkeeping.
What qualifies as a business?
You won’t have to keep receipts for all your utility bills or do the math to allocate those expenses to your home office. You can use the easier method of calculating your home office expenses by using the simplified method. For example, assume you use an extra bedroom as your home office.



No comments:
Post a Comment